MODIFIED ON: November 29, 2022 / ALIGNMINDS TECHNOLOGIES / 0 COMMENTS
An era without software seems to have been a millennium ago. We are used to software like never before. Be it creating a meeting appointment or switching on your air conditioner before you get home, software is an integral part of our life.

What is the future of app development and what will be the role Microservices Architecture?
Traditional software development has been following a monolithic approach. Any change will require the whole system to be updated. For example, if you run an ERP software and you want to make a change to the purchase module only, you’ll have to upgrade the rest of the software as well. It’s a single code base with multiple modules bundled together. However, this approach brings in a lot of disadvantages
- Over a period of time, this becomes complex and impossible to manage.
- Developers find it difficult to understand.
- Modules are tightly coupled, eliminating the possibility of reuse.
- Increases the risk of failure.
- Testing is slow due to the higher amount of regression to be performed.
- IDEs and Web servers tend to get overloaded due to monolithic code.
- A high degree of coordination is required to scale development.
- Results in long term lock-in of technologies.
- Difficult to scale the application.
The result is that it takes ages to develop and deploy even small releases or bug fixes causing huge expenses and missed market opportunities.
The smartphone revolution in the latter part of the last decade has placed cutting edge software in the hands of the consumers. People are using mobile apps for everything they do – shopping, health, entertainment, work and securing their home. Every enterprise out there is looking to woo the consumers and get a share of the pie. Global IT spend is expected to touch $4 Trillion in 2022 after factoring in the expected decline in 2020 due to COVID-19 situation.
In today’s dynamic and competitive market, it is all the more important for software providers to be able to quickly and continuously release product updates and bug fixes. And where the traditional methods fail to deliver, newer ideas like Microservices are taking centre stage.
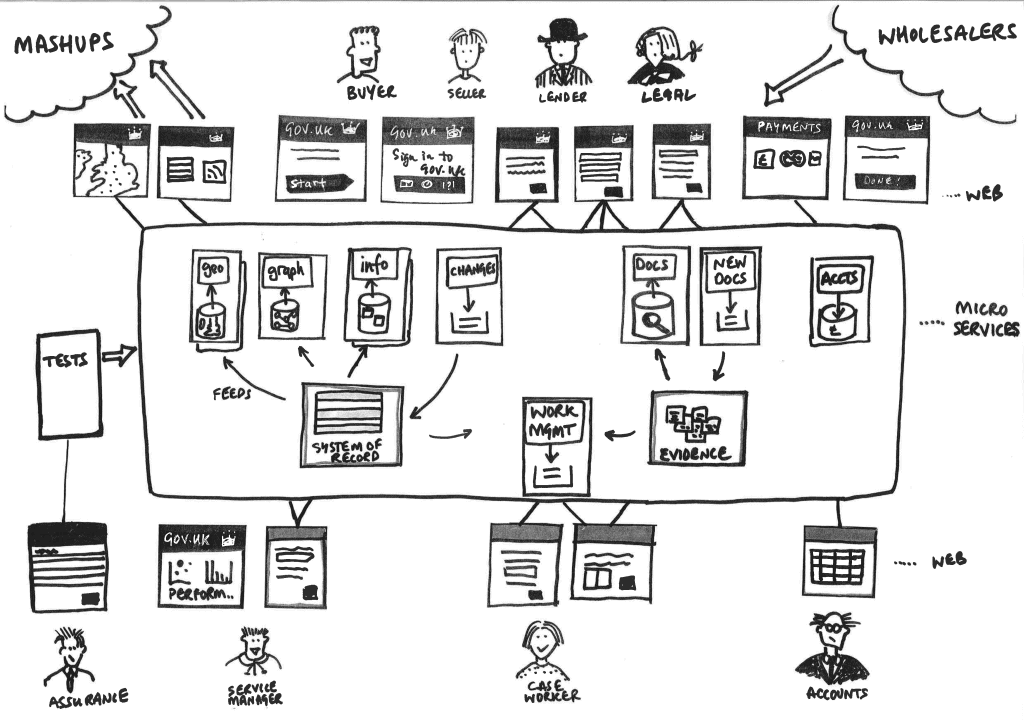
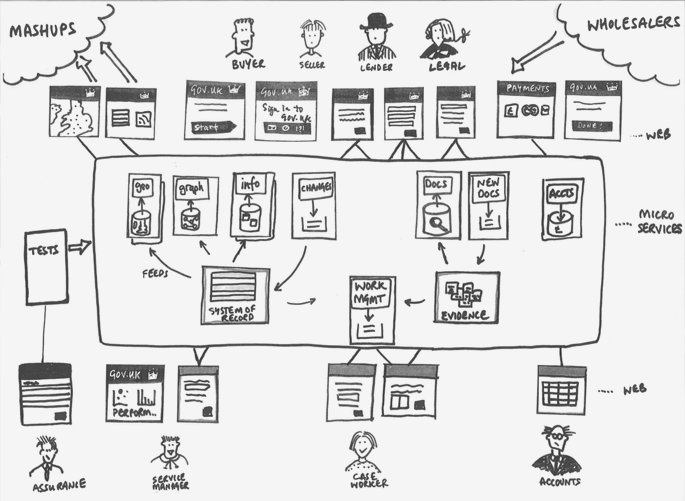
What are Microservices?
Microservices, by definition, is an architectural style in which the application is a collection of loosely coupled services. In Microservices architecture, a large application is divided into small modular services and have the following characteristics –
- Services are technology agnostic and use light weight protocols to communicate.
- Services are organised around specific business capabilities.
- Services are small in size, autonomously maintainable and independently deployable.
- Services are built and released with automated processes.
What are the advantages of Microservices?
The advantages of breaking an application into different smaller services are numerous.
1. Modularity and simpler development
Each Microservice is a small module. Hence it is easy to understand, develop and test.
2. Scalability
Microservices are implemented and deployed independently of each other. Since they are independent processes, they can be monitored and scaled independently.
3. Empowered teams and distributed development
Microservices can be developed, deployed and scaled in parallel by small autonomous teams. Each team is empowered to make architectural decisions. The architecture of each service evolves independently to achieve the best results.

Microservices architecture helps with building and deploying application faster.
4. Build and deploy faster
Microservices architecture employs continuous integration, continuous delivery and deployment. This significantly reduces time to market and human errors.
5. Isolation of services and reduced risk of failure
Since Microservices are modular and independent, there is a reduced risk of overall system failure. Isolated services are easier to debug and fix.
6. Freedom to try different technologies
Since Microservices are technology agnostic, each service could be implemented in a different technology, whichever is best suited to the business function being performed. Sometimes, the choice could be based on the knowledge levels of available developers. A service written in Node.js works harmoniously with one written in Go. The focus is on implementing the business capabilities and not technology.
7. No long-term lock-in of technologies
Microservices are sufficiently small and independent. Hence it is easy to implement a service in new technology and replace the old one when the technologies become obsolete. It is easy to upgrade without impacting the system.
Companies like Amazon, Netflix, eBay, Coca-Cola, PayPal, Walmart, Spotify and many more have refactored their applications into Microservices. We are seeing deeper integration of microservices offerings in Google Cloud, AWS and Azure. AWS Lambda is a great example of serverless microservices. Microservices style of architecture is gaining traction quickly as the preferred method of implementing applications throughout industrial verticals. Companies are embracing innovation to increase the efficiency of product teams and reduce development and deployment times. With its rapid adoption rate, it is predicted that Microservices will become the default architecture for applications in the years to come.
This article is written by Madhu M Peringote, Director of Technology at AlignMinds Technologies
Leave a reply
Your email address will not be published.
-
Recent Posts
- The Ultimate 4-Step Guide to Modernizing Your Applications
- The 12 Most Popular Computer Vision Tools in 2024
- How MLOps is Transforming Businesses in 2024
- The Ultimate Guide to Product Engineering Services for Businesses
- 5 Top Use Cases of Computer Vision in the Hospitality Industry
-
Categories
- MVP Development (5)
- AlignMinds (55)
- Operating Systems (1)
- Android POS (3)
- Application Hosting (1)
- Artificial Intelligence (23)
- Big Data (2)
- Blockchain (1)
- Cloud Application Development (7)
- Software Development (29)
- Software Testing (9)
- Strategy & User Experience Design (4)
- Web Application Development (23)
- Cyber Security (6)
- Outsourcing (7)
- Programming Languages (3)
- DevOps (5)
- Software Designing (6)
- How to Code (4)
- Internet of Things (1)
- Machine Learning (2)
- Mobile App Marketing (4)
- Mobile Application Development (18)
- Mobile Applications (5)







